Tig Vs Mig Welding | What’s the Difference?
Can you think of many objects that aren’t made with welded parts or welded themselves? It’s a hard task. We know welding is an integral part of the manufacturing process, but with so many different methods, it can be hard to understand the difference or determine which method is best. Most industrial companies stay on top of the advancements and changes in welding styles and techniques, but some don’t know where to start. Whether you’re unfamiliar or just in need of a refresher, read on for the differences between the most common welding methods used in manufacturing.
Welding 101
The concept of welding dates back to the medieval period with the heat and hammer process known as “forge welding.” Fast forward to the last 100 years and we can see the development of almost all of the modern welding innovations we have today. We’re now faced with a variety of welding methods – each with their own pros and cons. The two main welding methods related to our industry are MIG and TIG, but we will also cover another major method, Stick welding. The chosen method should depend on the metal, environment, application, speed and more.
What is MIG Welding?
Also known as Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAW), MIG welding is the most common type of welding used by custom automation and manufacturing professionals.
Metals:
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
- Aluminum Alloy
Chosen for:
- Speed
- Flexibility
- Minimal Clean-up
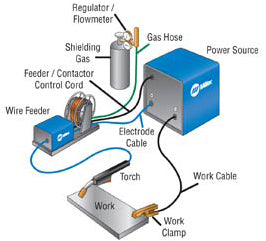 MIG welders utilize a wire welding electrode that is automatically spool fed at a constant speed. The electrical current between the wire and metal surface creates an arc that melts the wire and aids in the creation of a high-strength weld with little cleaning. An inert shielding gas flows through the welding gun along with the electrode and protects the weld from contamination. MIG welding can be used on stainless steel, mild steel, and aluminum as thin as 26-gauge and also on much thicker pieces as well. It’s probably the easiest method to learn and results in good looking, strong welds. Minimal clean-up is required, meaning little to no grinding or sanding. It’s the go-to method for our welding services.
MIG welders utilize a wire welding electrode that is automatically spool fed at a constant speed. The electrical current between the wire and metal surface creates an arc that melts the wire and aids in the creation of a high-strength weld with little cleaning. An inert shielding gas flows through the welding gun along with the electrode and protects the weld from contamination. MIG welding can be used on stainless steel, mild steel, and aluminum as thin as 26-gauge and also on much thicker pieces as well. It’s probably the easiest method to learn and results in good looking, strong welds. Minimal clean-up is required, meaning little to no grinding or sanding. It’s the go-to method for our welding services.
Flux Core Arc Welding (FCAW) is a variation of MIG welding that is very similar, but does not require a shielding gas. Instead, it feeds a Flux-Cored wire to shield the arc as a simple approach that works well in heavily windy conditions or on dirty metals. It can be used on similar metals and in a variety of thicknesses. While this process is not widely used in manufacturing, it is mostly used in construction because of its speed and portability.
What is TIG Welding?
TIG welding, also known as Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW), is another arc based welding process that uses a non-consumable tungsten electrode to create the weld. Unlike MIG, filler wire is applied by hand.
Metals:
- Stainless Steel
- Mild Steel
- Aluminum alloys
- Titanium*
- Chromoly*
- Copper*
- Brass*
- And more
* Indicates metals used exclusively with this method.
Chosen for:
- Highest Quality
- Best Looking Finish
- No Clean-Up
- Widest Variety of Metal types and sizes
- Thinner Metals
As the longer name implies, this method also uses a shielding gas (often argon) and filler metal to protect the weld area from contamination. TIG welding is much harder to master and significantly slower than other methods, but it provides the greatest control capability which allows for stronger and higher quality welds. As an added benefit, it’s also the cleanest method and often requires no excessive clean-up.
there are few things more visually appealing in our industry than quality stainless or aluminum TIG welds. Often referred to as “stacking” or “laying dimes”, skilled welders are creating welds that are as much aesthetic as they are structural.
What is Stick Welding?
Also known as Arc or Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW), Stick welding is the most basic form of welding, but not necessarily the easiest to grasp. It is easy to master and very common in both heavy construction and at home.
Metals:
- Stainless Steel
- Steel
- Cast Iron*
* Indicates metal used exclusively with this method.
Chosen for:
- Thicker Metals
- Outdoor / Windy Environments
- Forgiveness with Dirty or Rusty Metals
Stick welding requires no gas but uses a consumable electrode “stick” that flows electric current between it and the metal surface. In some applications, the most common 1/8th-inch diameter electrode can be consumed in just one minute. It is still considered the most economical method. You’ve likely seen this type used in heavy-duty applications on ships, tractors, and more. That is because stick welding is best suited for thicker metal, usually with thicknesses of 18 gauge or more. Unlike the other methods, stick welding produces a lot of slag – the excess splatter you’ve probably seen during the welding process – and requires significant clean-up. It is the least common method used in general manufacturing, but good for applications that don’t require a clean finish.
Welding Resources
Welding is a diverse and continuously evolving process. There are many more methods and variations not discussed here. This article was created to provide an overview of the most common welding methods used in custom automation and manufacturing and backed by the resources of Miller. If you’d like to know more, we recommend heading to MillerWelds.com. Since 1927, they’ve been an industry leader in welders and welding knowledge.
Our Engineered Solutions group contains a comprehensive machine shop with a team of experienced fabricators armed with Miller welders. Whether you want a turnkey product or just metal fabrication, let us to put our welding services to work for you. We’re always ready to support American manufacturing.
Your Welding Questions, Answered
Feel free to contact us with any specific questions you may have regarding welding or anything custom manufacturing.
BONUS Spotlight for existing professionals: Learn to go lean with your own welding operations
And in case you’re like us and can’t get enough of welding photos, here are a few more.





